| |
|
|
| |
A flower is the the complex
sexual reproductive structure of
Angiosperms,
typically consisting of an axis bearing
perianth parts,
androecium
(male) and gynoecium (female).
|
|
| |
|
|
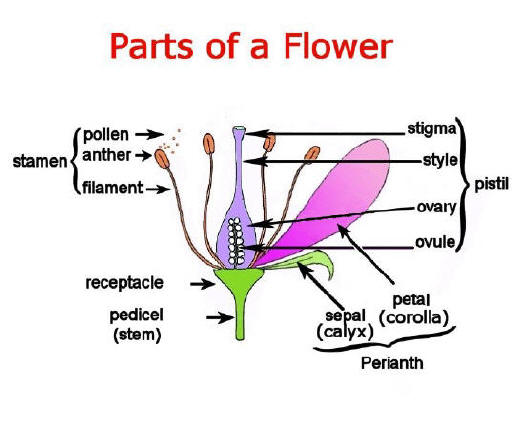 Bisexual flower show four distinctive parts arranged in rings inside
each other which are technically modified leaves:
Sepal,
petal,
stamen &
pistil. This flower is referred to as complete (with all four parts) and
perfect (with "male" stamens and "female" pistil). The
ovary ripens into
a fruit and the
ovules inside develop into
seeds. Bisexual flower show four distinctive parts arranged in rings inside
each other which are technically modified leaves:
Sepal,
petal,
stamen &
pistil. This flower is referred to as complete (with all four parts) and
perfect (with "male" stamens and "female" pistil). The
ovary ripens into
a fruit and the
ovules inside develop into
seeds.
Incomplete flowers are lacking one or more of the four main parts.
Imperfect (unisexual) flowers contain a pistil or stamens, but not both.
The colourful parts of a flower and its scent attract
pollinators and
guide them to the nectary, usually at the base of the flower tube. |
|
Androecium
(male Parts or stamens)
It is made up of the filament and anther, it is the pollen producing part
of the plant.
Anther
This is the part of the stamen that produces and contains pollen.
Filament
This is the fine hair-like stalk that the anther sits on top of.
Pollen
This is the dust-like male reproductive cell of
flowering plants.
Gynoecium
(female Parts or
carpels or pistil)
It is made up of the stigma,
style, and ovary. Each pistil is constructed of one to many rolled leaflike structures.
Stigma
This is
the part of the pistil which receives the pollen grains and on
which they germinate.
Style This is the long stalk that the
stigma sits on top of.
Ovary
The part of the plant that contains
the ovules.
Ovule
The part of the ovary that becomes the seeds.
Petal
The colorful, often bright part of the flower (corolla).
Sepal
The parts that look like little green leaves that cover the outside of a
flower bud (calix).
(Undifferentiated "Perianth segment" that
are not clearly
differentiated into sepals and petals, take the names of
tepals.)
Flower may also be considered for other characteristic:
-
Perfect:
A flower that has both the male parts and female parts in the same
flower. Examples: most
cacti.
-
Imperfect:
A flower that has either all male parts or all female parts, but not
both in the same flower. (Plant bearing imperfect flowers may be
monoecious (with male and female flowers on the same plant)
and
dioecious (whit male and female flowers on diferent plants)
-
Hypogynous
With
perianth and stamens
positioned
below the pistil
-
Perigynous
With
perianth and stamens
positioned
around the pistil
-
Epigynous
With
perianth and stamens
positioned
above the pistil
|